A look at the changing landscape
The rapid and relentless advance of artificial intelligence (AI) has ignited apprehensions about its impending impact on the job landscape. Amid the heated debates surrounding the potency of AI in outperforming human capabilities and potentially supplanting jobs, a fresh report has surfaced, illuminating a disquieting prospect of various professions being squarely in the crosshairs of AI's disruptive technology.
The McKinsey Global Institute has recently unveiled a comprehensive study titled “Generative AI and the Future of Work in America,” providing a deep dive into the potential repercussions of AI on the American job market. The report’s findings underscore a paradigm shift driven by the synergy of AI breakthroughs and evolving consumer behavior, poised to reshape the contours of employment across multifarious sectors and compel the workforce to chart new career trajectories. The report emphasizes the seismic potential of AI in catalyzing economic automation, with projections indicating that AI could permeate nearly 30% of labor hours in the U.S. economy by 2030.
Occupational transitions: roles most susceptible to AI encroachment
Anticipating the transformative wave, the report posits that roles tethered to routine tasks and data-driven activities are the most susceptible to AI’s encroachment in the quest for operational optimization. Sectors like administrative support, customer interaction services, and the culinary domain are anticipated to bear the brunt of this transition, potentially triggering a demand for approximately 12 million occupational shifts within the U.S. by 2030 (see Figure 1).
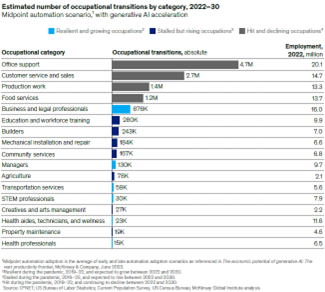
Other roles, such as those involving data aggregation and repetitive functions, common to roles such as clerks, retail salespersons, administrative assistants, and cashiers, are poised to be seamlessly integrated into AI-driven systems. Such a transformation would enhance efficiency by harnessing automated systems for activities characterized by repetitive patterns and elementary data manipulation. This burgeoning transformation will necessitate an agile workforce capable of navigating through uncharted professional territories. The report estimates that around 11.8 million workers currently engaged in fields marked by dwindling demand would need to embrace alternative career paths by the dawn of the next decade.
Paradigm shift: retraining and upskilling is cornerstone to survival
Underpinning the analysis is the observation that the looming shift will have a disproportionate impact on lower-income workers. Those earning less than $30,800 annually, as well as those within the $30,800 to $38,200 bracket, face an outsized tenfold to fourteenfold likelihood of undertaking vocational transitions compared to higher-income counterparts. The report accentuates the need for a paradigm shift in the skill sets of these individuals, indicating that adapting to evolving technological paradigms is the cornerstone of survival in the dynamic job market. This underscores the importance of upskilling in facilitating a harmonious coexistence between humans and AI-driven technologies.
The report also clarifies this transformation will not transpire overnight. Rather, it will create opportunities for professionals in STEM fields, creative endeavors, business endeavors and legal arenas. The demand for STEM roles is anticipated to experience a robust surge of 23% by 2030 (see Figure 2). Despite headline-grabbing layoffs witnessed in the tech sector during 2023, the report emphasizes the lasting need for tech-savvy talents across industries of varying sizes as the economy steers further towards digitalization.
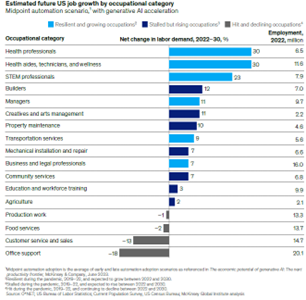
Furthermore, the report shines a light on the health care sector, projecting substantial job growth. An estimated 3.5 million positions are expected to emerge, encompassing roles such as health aides, health care technicians and wellness practitioners. Industries spanning banking, insurance, pharmaceuticals, health care and transportation services are poised to undergo profound digital metamorphoses, consequently fueling robust job creation in these domains.
Higher education qualifications and specialized skill sets take center stage
The report concludes by asserting that growth will primarily manifest in roles mandating higher educational qualifications and specialized skill sets. Educational systems need to prepare workers for the jobs of the future, with different resources and tools at their disposal. We will see continued amplification of job prospects for roles demanding intricate problem-solving, critical analysis, creative acumen, and advanced technical prowess, while roles predominantly defined by monotonous manual tasks will likely diminish.
Here at the University of St. Thomas, we are helping professionals and career changers chart their career trajectory in the software field. All our courses are taught by seasoned veterans; we teach our students hands-on applied learning – they learn practical skills from Day 1. This applied learning opens the door for many more individuals to participate in the digital revolution. As the industry continues to evolve, the knowledge and skills gained through our graduate programs in software prepare students for the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead.
Author bios:

Manjeet Rege is a professor and chair of the Department of Software Engineering and Data Science at the University of St. Thomas. Rege is an author, mentor, thought leader, and a frequent public speaker on big data, machine learning, and artificial intelligence technologies. He is also the co-host of the “All Things Data” podcast that brings together leading data scientists, technologists, business model experts and futurists to discuss strategies to utilize, harness and deploy data science, data-driven strategies and enable digital transformation. Apart from being engaged in research, Rege regularly consults with various organizations to provide expert guidance for building big data and AI practice, and applying innovative data science approaches. He has published in various peer-reviewed reputed venues such as IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, Data Mining & Knowledge Discovery Journal, IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, and the World Wide Web Conference. He is on the editorial review board of Journal of Computer Information Systems and regularly serves on the program committees of various international conferences.







